Are you wondering about the differences between DNA and RNA? Look no further! Our DNA vs RNA Venn Diagram breaks down the similarities and differences between these two important nucleic acids. From their molecular structure and location in the cell to their functions and stability, this Venn diagram covers it all. Get a comprehensive understanding of DNA and RNA with this informative and visually appealing resource.
DNA vs RNA Venn Diagram
Here is a Venn diagram that illustrates the differences between DNA and RNA:
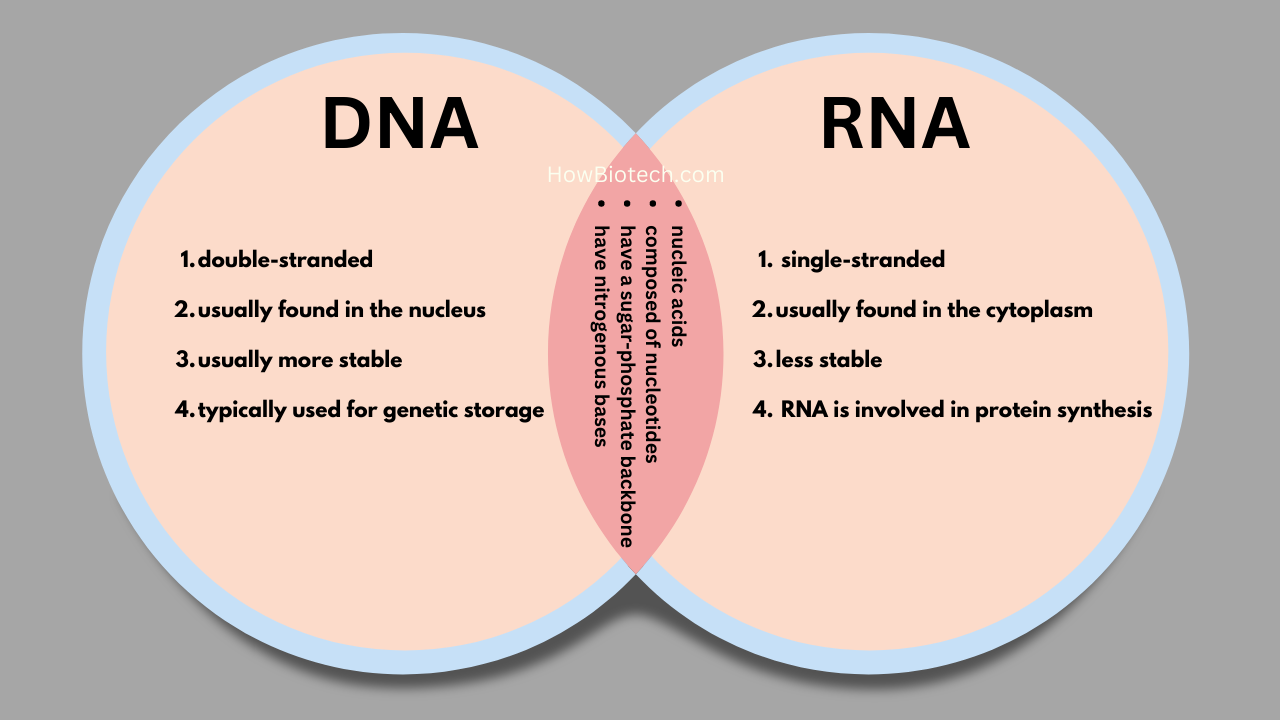
In this DNA vs RNA Venn Diagram, the overlap between the two circles represents the shared characteristics of DNA and RNA, while the areas outside the overlap represent the unique characteristics of each molecule.
Some of the shared characteristics of DNA and RNA include:
- Both are nucleic acids
- Both are composed of nucleotides
- Both have a sugar-phosphate backbone
- Both have nitrogenous bases
Some of the differences between DNA and RNA include:
- DNA is double-stranded, while RNA is usually single-stranded
- DNA is usually found in the nucleus, while RNA is usually found in the cytoplasm
- DNA is usually more stable and longer-lived than RNA
- DNA is typically used for genetic storage, while RNA is involved in protein synthesis and other functions
Students also read:
- Banana DNA Extraction
- Why is DNA Extraction Important?
- How is DNA Packaged in the Nucleus? (Explained with Images!)
Overall, DNA and RNA are similar in many ways, but they have some key differences that make them important for different functions within the cell.
Comparison Table of DNA and RNA
Here is a comprehensive comparison table of DNA and RNA:
| Characteristic | DNA | RNA |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular structure | Double-stranded helix | Single-stranded, often with secondary structure |
| Sugar | Deoxyribose | Ribose |
| Nitrogenous bases | Adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine | Adenine, guanine, cytosine, uracil |
| Function | Genetic storage | Protein synthesis, gene expression, and other functions |
| Location | Nucleus | Cytoplasm, sometimes also found in the nucleus |
| Stability | More stable and longer-lived than RNA | Less stable and shorter-lived than DNA |
| Replication | Replicated by DNA polymerase | Transcribed by RNA polymerase |
Overall, DNA and RNA are similar in many ways, but they have some key differences that make them important for different functions within the cell. DNA is a double-stranded molecule that is responsible for storing genetic information, while RNA is a single-stranded molecule that is involved in protein synthesis and other functions. DNA is found in the nucleus, while RNA is found in the cytoplasm and is involved in the expression of genetic information.
Functions of DNA
Here are some of the functions of DNA:
- Genetic storage
- Gene expression
- Protein synthesis
- DNA replication
- DNA repair
- Regulation of gene expression
- Control of cell division
- Determining inherited characteristics and traits
DNA is a complex and multifunctional molecule that plays a central role in the functioning of cells. It is the molecule that carries the genetic instructions needed for the development, growth, and functioning of all living organisms. DNA is found in the cells of all living things and is organized into structures called chromosomes. It is essential for the accurate replication and expression of genetic information, and it is involved in a wide range of important cellular processes.
Functions of RNA
Here are some of the functions of RNA:
- Protein synthesis
- Gene expression
- Regulation of gene expression
- RNA splicing
- RNA editing
- Transport of proteins
- Catalysis
- Transport of genetic information
- Control of gene expression
RNA is a complex and multifunctional molecule that plays a central role in the functioning of cells. It is involved in a wide range of important cellular processes, including protein synthesis, gene expression, and regulation of gene expression. RNA is found in the cytoplasm of cells, and it is involved in the expression of genetic information from DNA. It is also involved in the synthesis of proteins, which are essential for the structure and function of cells. RNA is a key molecule in the flow of genetic information from DNA to protein, and it plays a central role in the regulation of gene expression.
People Also Read: